For product information and pricing, Chat with sales agent:
or email us : sales@clirik.com
Click links below to see related products.


Coal gangue, a byproduct of coal mining and washing operations, has long been considered an environmental challenge.
However, advancements in coal gangue processing have opened new avenues for utilizing this waste material.
Among the various stages in coal gangue processing, the grinding process stands out as a crucial step with transformative potential.
The Role of Grinding in Coal Gangue Processing:
The primary objective of grinding coal gangue is to reduce its particle size.
This process transforms the raw, often coarse material into finer particles, opening up opportunities for diverse applications.
Finer particles resulting from grinding can significantly improve the reactivity and suitability of coal gangue in various applications.
Industries, particularly construction, have started to recognize the value of finely ground gangue in the production of building materials.
Several grinding equipment options are available for coal gangue processing, each with its unique advantages.
Ball mills, Raymond mills, vertical roller mills, and ultrafine grinding mills are among the common choices.
Selection depends on factors such as desired particle size, production capacity, and energy efficiency.
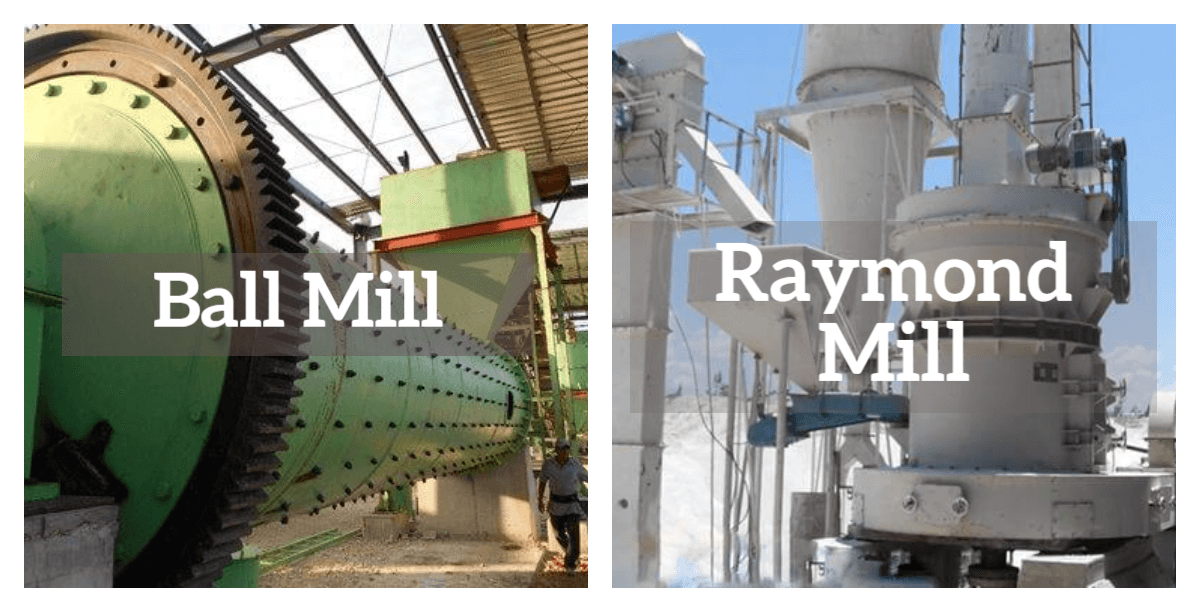
Ball Mills:
Mechanism: Ball mills operate by rotating a cylindrical vessel filled with grinding media, such as steel balls. The coal gangue is introduced into the mill, and the collision and attrition between the balls and gangue particles result in size reduction.
Applications: Ball mills are versatile and widely used, suitable for both coarse and fine grinding. They find application in various industries, from cement production to mineral processing.
Raymond Mills:
Mechanism: Raymond mills utilize a set of rotating rollers to crush and grind coal gangue between them. The material is fed into the grinding zone, and the rollers exert pressure to achieve the desired fineness.
Applications: Renowned for their efficiency in achieving finer particle sizes, Raymond mills are commonly employed in the production of high-quality building materials and advanced industrial applications.

Ultrafine Grinding Mills:
Mechanism: Ultrafine grinding mills, such as jet mills and stirred media mills, operate on the principle of interparticle comminution. High-speed jets or stirring mechanisms create intense forces that break down coal gangue into ultrafine particles.
Applications: Ideal for applications demanding extremely fine particle sizes, these mills are at the forefront of technological advancements in coal gangue processing. They cater to industries requiring materials with superior reactivity and performance.
Vertical Roller Mills:
Mechanism: Vertical Roller Mills consist of a rotating table onto which the coal gangue is fed. The grinding rollers crush and grind the material, and the ground particles are swept upwards by the airstream for further classification.
Applications: VRMs are acclaimed for their energy efficiency and ability to produce a narrow particle size distribution. They are often preferred in industries aiming for precise control over product quality.
Finely ground coal gangue can be incorporated into cement or concrete mixes, imparting unique properties to the final product.
This not only reduces the reliance on traditional raw materials but also addresses environmental concerns associated with waste disposal.
The grinding process requires rigorous quality control measures to ensure the consistency and performance of the end product.
Regular sampling and testing help monitor the particle size distribution and other critical characteristics, ensuring that the processed gangue meets required specifications.
Dust control during grinding is imperative to minimize environmental impact.
The use of enclosed grinding systems, dust collectors, and water sprays are common strategies to mitigate airborne dust, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment.
As sustainability becomes a focal point in industrial processes, optimizing energy efficiency in grinding operations is paramount.
Selecting equipment with lower energy consumption and implementing smart process controls contribute to both environmental and economic sustainability.
Case Studies:
In regions where coal gangue is abundant, industries are experimenting with incorporating finely ground gangue into cement and concrete.
This not only reduces the environmental footprint but also leads to the development of innovative, sustainable construction materials.
Some coal gangue processing plants are exploring the utilization of finely ground gangue as a fuel in power generation.
Advanced combustion technologies ensure efficient energy extraction while addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional coal combustion.
The grinding process in coal gangue processing emerges as a pivotal stage, driving the transformation of this waste material into a valuable resource.
As industries explore innovative applications and sustainable practices, the significance of finely ground coal gangue becomes increasingly apparent.
Through efficient grinding and careful utilization, coal gangue can contribute to the development of environmentally friendly building materials and cleaner energy sources, marking a paradigm shift in the perception of this once-disregarded byproduct.
