For product information and pricing, Chat with sales agent:
or email us : sales@clirik.com
Click links below to see related products.
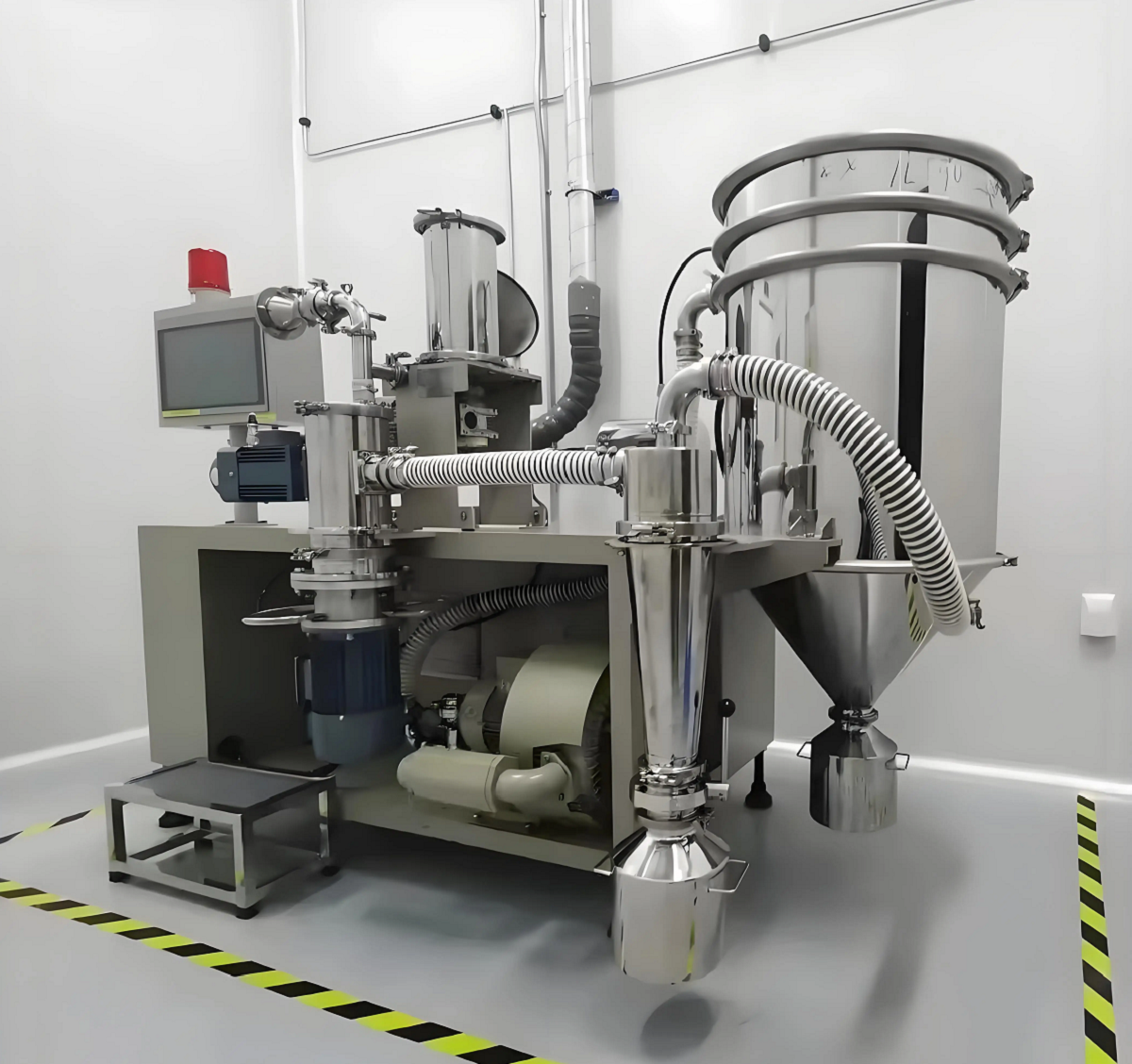
The jet mill uses the energy of high-speed air flow to impact, rub and shear materials, thereby achieving ultra-fine grinding and classification. It can process a variety of materials such as metal and alloy powders, ceramics and fillers, chemical raw materials, food and medicine, new energy materials and other materials, and are suitable for a variety of industries and fields.
The jet mill utilizes the energy of high-speed airflow or superheated steam to cause particles to impact, collide, and rub against each other, achieving ultrafine grinding.
It has no moving parts during the grinding process, making it easy to maintain. Its fully enclosed operation eliminates impurities, resulting in products with excellent particle size distribution, shape, purity, and dispersion.
Jet mills are widely used in a variety of industries, including chemicals, mining, abrasives, refractory materials, battery materials, metallurgy, building materials, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, food, pesticides, feed, new materials, and environmental protection.
For example, in the chemical industry, they can be used to prepare ultrafine catalysts to increase petroleum cracking rates; in the pharmaceutical industry, they are used to refine drugs to enhance absorption; and in the food processing industry, they can be used to process fiber-rich diets and calcium-supplemented foods.

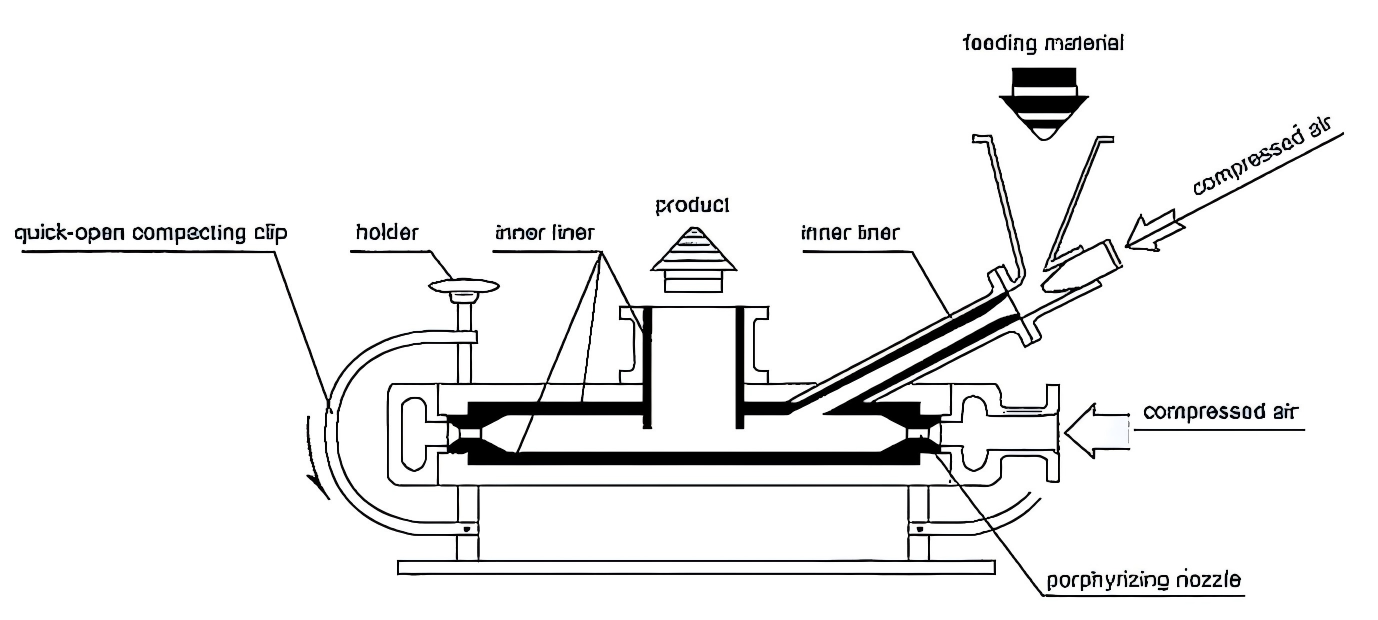
During operation, compressed air is chilled, filtered, and dried before flowing through nozzles in a supersonic flow into the crushing chamber, causing the material to flow and accelerate.
The material experiences severe collision, friction, and cutting at the intersection of multiple nozzles, resulting in ultra-fine particle crushing.
The crushed material is transported by the rising airflow to the impeller classification zone, where the centrifugal force of the classifier and the pumping force of the fan separate the coarse and fine powders.
The coarse powder returns to the crushing chamber for further crushing, while the qualified fine powder is carried by the airflow into the cyclone collector.
The bag filter collects fine dust, and the induced draft fan discharges the purified air.
High grinding precision: Ultra-fine grinding is achieved, resulting in a narrow particle size distribution.
Low wear: Materials are crushed through mutual collision, minimizing impact and wear on the equipment's inner walls.
Clean and environmentally friendly: The entire system features enclosed grinding, resulting in low dust and noise.
High degree of automation: The control system utilizes programmable control for easy operation.
Wide application: Suitable for processing materials with a Mohs hardness of 1-10.

The jet mill is suitable for dry grinding of various materials with Moh's hardness below 9, especially for materials with high hardness, high purity and high added value.
Jet mills are widely used in a variety of industries, including chemicals, mining, abrasives, refractory materials, battery materials, metallurgy, building materials, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, food, pesticides, feed, new materials, and environmental protection.
For example, in the chemical industry, they can be used to prepare ultrafine catalysts to increase petroleum cracking rates; in the pharmaceutical industry, they are used to refine drugs to enhance absorption; and in the food processing industry, they can be used to process fiber-rich diets and calcium-supplemented foods.

| Model | Type | Capacity (kg/h) | Compressed Air Consumption (m³/min) | Compressed air pressure(Mpa) | Application |
| YQ50MINI | Laboratory-grade jet mill | 0.1-1 | 0.5 | 0.6-0.8 | Research and development stage of chemical APIs; micronized powders for inhalation preparations |
| YQ75 | Laboratory-grade jet mill | 0.3-5 | 1 | 0.6-0.8 | Research and development stage of chemical raw materials; micronized excipients for inhalation preparations |
| YQ100-1 | Small jet mill | 0.8-6 | 2 | 0.6-0.8 | R&D stage of chemical raw materials; small-scale crushing of fine chemical materials; R&D stage of powdered cosmetic raw materials; crushing stage of new materials and polymer materials |
| YQ150 | Small jet mill | 0.8-8 | 3 | 0.6-0.8 | From the R&D stage to the pilot stage of chemical APIs |
| YQ200 | Medium jet mill | 5-30 | 5 | 0.6-0.8 | Pilot stage of chemical APIs; small-scale production of chemical APIs; micronized excipients for inhalation preparations; pilot stage of powdered cosmetic raw materials; production of new materials and polymers |
| YQ300 | Mass production grade air jet mill | 8-50 | 6-7 | 0.6-0.8 | Production of chemical APIs; micronized excipients for inhalation preparations; powdered cosmetic raw materials; production of new materials and polymers |
| YQ350 | Mass production grade air jet mill | 30-200 | 9-11 | 0.6-0.8 | Production of chemical APIs; micronized excipient powders for inhalation preparations; powdered cosmetic raw materials; production of new materials and polymers |
| Higher-capacity air jet mill | 20 | 0.6-0.8 | Production of chemical APIs; production of new materials and polymers | ||
| LQ150 | Small fluidized bed jet mill | 0.8-8 | 3 | 0.6-0.8 | R&D stage of chemical APIs; R&D stage of pulverization of new materials and polymers |
| LQ300 | Mass production grade fluidized bed jet mill | 10-50 | 7 | 0.6-0.8 | Production of chemical APIs; production of new materials and polymers |
| Higher-capacity fluidized bed jet mill | 20 | 0.6-0.8 | Production of chemical APIs; production of new materials and polymers | ||
| FWJ150 | Small grading ultrafine pulverizer | 0.8-8 | R&D stage of herbal medicines and chemical APIs; R&D stage of fine chemicals and new materials | ||
| FWJ300 | Mass production grading ultrafine pulverizer | 30-300 | Production of herbal medicines and chemical APIs; production of fine chemicals and new materials | ||
| Higher-capacity ultrafine pulverizer | 100-1000 | Production of herbal medicines and chemical APIs; production of fine chemicals and new materials |